Cryptocurrencies
6 de fevereiro de 2024Cryptocurrencies are a form of decentralized digital currency that utilize cryptographic techniques to ensure secure transactions and manage the creation of new units. Since the inception of Bitcoin in 2009, by an entity known as Satoshi Nakamoto, cryptocurrencies have gained global popularity and recognition. In this article, we will delve into how cryptocurrencies operate, including the underlying principles, the technology behind them, and their impact on the global financial landscape.
Core Principles
Decentralization:
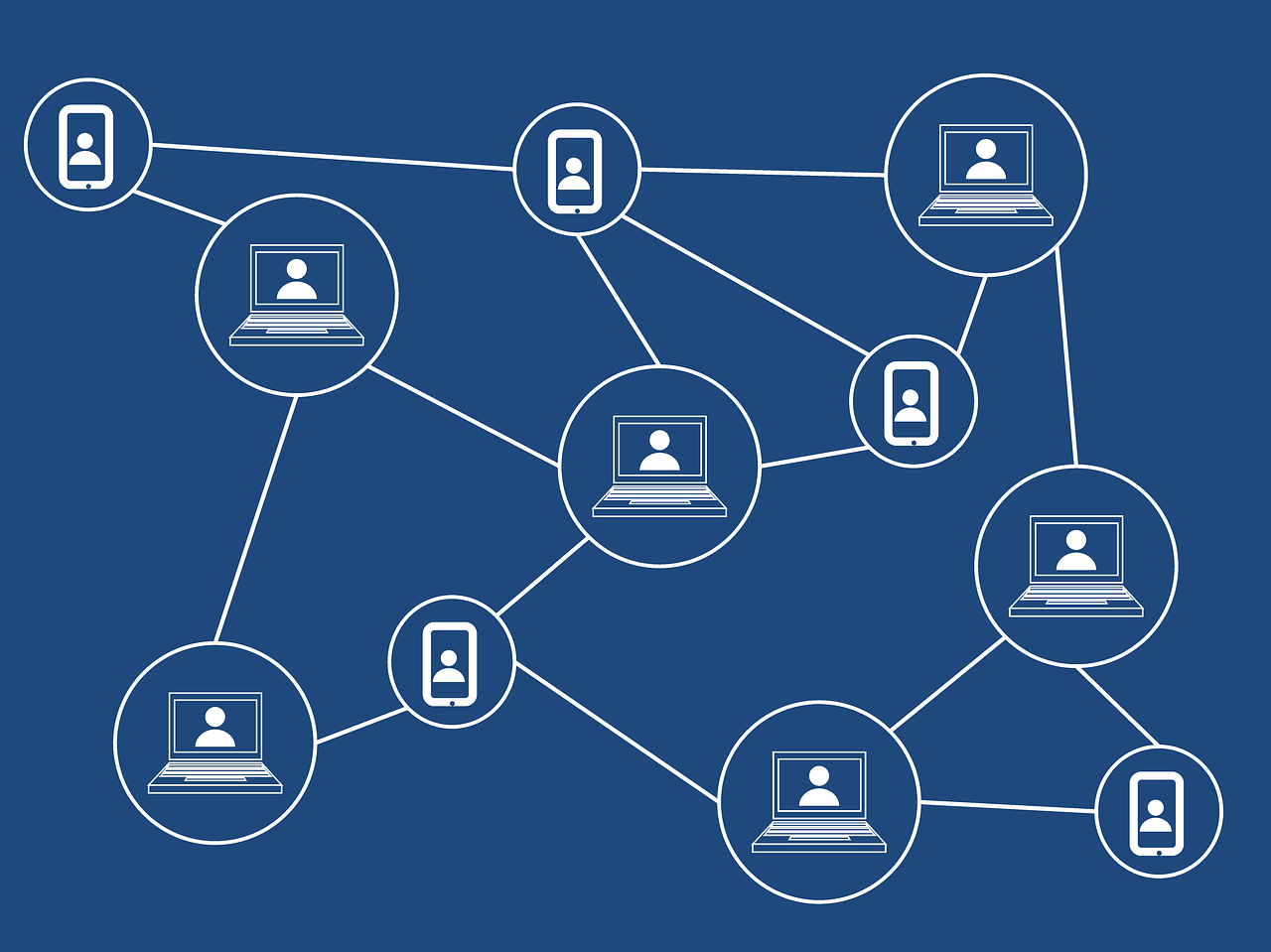
A fundamental characteristic of cryptocurrencies is their decentralization. This entails the absence of a central authority, such as a central bank, controlling transactions or the issuance of new units. Instead, transactions are recorded on a public ledger known as the blockchain.
Blockchain:
The blockchain serves as a public record of all transactions of a specific cryptocurrency. Each block on the blockchain contains a set of transactions and is linked to the previous block through a cryptographic hash function. This ensures the integrity of the record, as any attempt to alter a block would require modifying all subsequent blocks, making it exceedingly difficult to execute.
Cryptography:
Cryptography is used to ensure the security of transactions and the creation of new cryptocurrency units. Cryptographic keys are employed to sign transactions, ensuring that only the legitimate owner of a cryptocurrency can spend it.
Technology Behind Cryptocurrencies
Proof of Work (PoW):
Most cryptocurrencies, including Bitcoin, utilize the Proof of Work algorithm to validate and record transactions on the blockchain. In this system, miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems, with the first to find the solution being rewarded with new units of the cryptocurrency.
Proof of Stake (PoS):
Another method of transaction validation is Proof of Stake, where validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. This method is considered more efficient than Proof of Work, as it consumes less energy.
Smart Contracts:
Some cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum, enable the execution of smart contracts. These contracts are self-executing programs that define the conditions of a transaction and are automatically executed when those conditions are met.
Impact on the Global Financial Landscape
International Transfers:
Cryptocurrencies offer a fast and cost-effective alternative for international money transfers, especially compared to traditional methods that can be slow and expensive.
Financial Inclusion:
For those without access to traditional banking services, cryptocurrencies can provide a way to participate in the global economy, provided they have access to the internet and a digital wallet.
Regulatory Challenges:
Cryptocurrencies face regulatory challenges in many countries due to concerns about money laundering, tax evasion, and price volatility. Some countries have banned or restricted their use, while others are developing regulations to address these issues.
Financial Innovation:
Despite challenges, cryptocurrencies have driven financial innovation, leading to the development of new products and services such as non-fungible tokens (NFTs), decentralized finance (DeFi), and digital identity solutions.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrencies represent a new form of money that is challenging traditional financial models. With their decentralization, innovative technology, and potential to democratize financial access, cryptocurrencies continue to attract the attention of investors, regulators, and innovators worldwide. However, it is important to recognize that they also pose significant challenges that need to be addressed for their full potential to be realized.